All of us might have experienced blood loss at some point in time. Bleeding is the loss of blood. It is okay to have a slight loss of blood without harmful effects. Typically, the actual amount of blood loss and its effects on you.
Bleeding can be external or outside the body, like getting a cut or wound. Sometimes it can be internal or inside the body -like when there's an injury to an internal organ. Some bleeding can be a disease symptom- like gastrointestinal bleeding, coughing up blood, or vaginal bleeding.
Providing blood for testing, nose bleeding, and normal menstruation does not create any significant blood loss. Whereas when someone is injured, undergoes surgery, or has a critical health condition, then the person could experience heavy blood loss.
When you start to bleed, a blood clot should form to stop bleeding. Later, the clot dissolves naturally. Sometimes, your body has problems related to clotting. These conditions are known as clotting disorders.
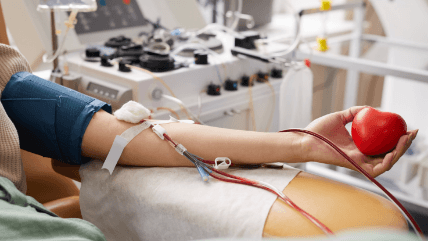
When blood loss becomes unmanageable, the patient requires blood from an external source to sustain life. This is when doctors make use of the donated blood.
A simple choice of donating blood can save countless lives and hopes.
COVID 19 and Blood Donation
Dr. Veena Shenoy, Associate Professor, Department of Transfusion Medicine, Amrita Hospital, says, "Blood donation can be made after 28 days of getting cured of Covid infection and after 14 days of either dose of the vaccination. Since the interval between the first and second doses is now 84 days, there is ample time for blood donation between the two doses. As there is a 14-day waiting period after each vaccination, the vaccination in the 18-45 years age group will not affect blood donor inflow. However, planning a blood donation before vaccination is a welcome step."
The blood donation process is simple as well as safe. It is a healthy practice and helps lower iron levels in your body, and regulates cholesterol and triglyceride levels. This can help people who require blood in situations like:
- Accidents, disasters, or other emergency situations
- Anemia induced by Thalassemia or sickle cell disease
- Blood loss during surgeries
- Cancer
- Complications during pregnancy and childbirth
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
However, you must meet some requirements to donate blood. Any healthy adult of age 18 to 60 years can donate blood in India. Men can donate once every three months, while women can donate once every four months. Other aspects need to be taken into account.
- Weight
- Normal Blood pressure
- Normal pulse
- Hemoglobin not less than 12.5 grams
- Free of complicated health conditions, sexually transmitted diseases, and other infections and diseases
- Those who have taken immunization shots or vaccinations should wait till the prescribed time
- The skin should be free from scars indicative of intravenous drug intake or recent blood donations
- Free from drugs or medications that may cause risk to the blood receiver
- Should not have taken tattoos in the last 12 months
- Should have not undergone surgery in the last six months
You can donate blood either in blood banks or outdoor blood donation camps. You should follow the necessary steps and guidelines during the blood donation procedure.
Blood Donation Scenario in Kerala
The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that at least 1% of any country's population must be donating blood to maintain an adequate blood supply. In India, the 1.38 billion population requires 13 million blood units, while our national average collection is just 11 million. However, Kerala collected 4.4 lakh units in 2019-2020, which can be considered adequate.
It is our responsibility to keep the blood banks filled with safe blood and save lives.
What Is Apheresis?
It is a special kind of blood donation that allows a donor to give specific blood components, such as platelets. We use the latest machines that collect and separate blood components for this purpose. A disposable kit is loaded into the machine. It automatically withdraws the desired amount of blood. During the donation process, the blood is drawn from one arm and channelled through the tube set to an automated system. This system separates and collects the platelets and safely returns the remaining blood components back to the donor. To stop the blood from clotting in the tubing, an anticoagulant is automatically mixed with the blood as it is pumped from the body into the apheresis machine. Platelets can be stored for only five days. Hence the need for platelet donation is huge and continuous.
Platelet Apheresis
Platelets are blood cells that are essential for the clotting of blood. They are routinely needed to support patients on chemotherapy, bone marrow transplants, organ transplants, hematological disorder, etc.
Can I Be an Apheresis Donor?
- If you meet the requirements for donating blood, you probably can give platelets.
- Your platelet count should be at least 1.5 lakhs/micro liter.
- The donor should have a minimum 60 kg body weight.
- You should not have taken aspirin or aspirin-containing medicine within the last 72 hours.
- The interval between platelet donations should be at least 2 days and the donor should not undergo apheresis more than twice per week or more than 24 times a year
- If you have taken any medicines recently, these should be discussed with the medical officer
- You should not have a fever, cold, flu, sore throat, or any other infection on the day of donation.
How Can I Prepare for Platelet Donation?
- Get a good night’s sleep.
- Have a good meal.
- Drink plenty of fluids before and after donation.
- Be prepared for no strenuous activity for the rest of that day.
Are Apheresis Donations Safe?
Yes. Donors are selected after medical examination and a few tests like platelet count, HCT, etc. Each donation is closely supervised throughout the procedure by our qualified and trained staff. Your body will replace the donated platelets within 48 hours. The kits which are used for the procedure are sterile and disposable.
Granulocyte Apheresis
It is a type of blood donation where white blood cells are given through an apheresis procedure. It is required for patients whose white blood cells are low due to chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
Stem Cell Apheresis
Peripheral stem cell apheresis has largely replaced bone marrow stem cell harvest for transplantation. Apheresis is performed after mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells from marrow to peripheral blood using growth factors. The stem cell apheresis procedure takes 4-5 hours. After a stem cell procedure, the donor has to wait six months for any future blood donation.







