Overview
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is a pioneering centre committed to the relentless pursuit of upgrading the treatment of epilepsy. Established in February 2010, our centre has become a beacon of hope for individuals affected by epilepsy all around the world.
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi has evolved into a hub that extends its healing touch to patients hailing from all corners of India, the Middle East, Africa, Asia Minor, and various Southeast Asian countries
Beyond serving as a premier treatment facility, Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has taken on the responsibility of knowledge dissemination and skill enhancement. The center has also emerged as an advanced epilepsy teaching centre for training neurologists, neurosurgeons, psychologists and technicians in the field - providing a strategy to help contain this globally devastating illness.
Our multidisciplinary team collaborates seamlessly to provide personalized and effective treatment. We recognize the profound impact that epilepsy can have on individuals and their families, and we are committed to offering not just medical treatment, but also support and educate our patients to empower and lead fulfilling lives.
Key Features:
- Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE) has the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in the country.
- AACE equipped with a high-density EEG system, a unique high-resolution scalp EEG
- India’s first in conducting the largest number of minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries
- Brain mapping research laboratory with scientists in collaboration with the clinicians
- Completed over 1000 epilepsy surgeries
- AACE is the first centre in India to develop and actively practice the technique of Stereo-EEG.
- Maximum number of intracranial EEG with this special technique of Stereo-EEG in this country
Disease Treated
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common disease that afflicts nearly 60 million people worldwide of which 6 million (10%) reside in India. Apart from being a physical disease, epilepsy has a strong mental and social implication. This disease adversely affects women with pregnancy and is an important contributor of learning disability in children. The incidence of divorce among epilepsy patients is on the rise. The unpredictability of epileptic attack leaves the patients helpless and most of the time at the mercy of others.
Drug-resistant epilepsy
Approximately one-third of patients whose seizures are not responsive to AEDs (drug-resistant epilepsies), can be cured of their seizures by surgical treatment (epilepsy surgery). Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE) provides comprehensive care to individuals who suffer from epilepsy. The Centre celebrated the successful completion of over 1000 epilepsy surgeries till date. Our team of experts include adult epileptologists, paediatricepileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, radiologists, nuclear medicine physician, neuroscientists, neuropathologist, neuropsychologist, medical social workers and dieticians.
Features
- Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit in the Country:
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi has the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in the country, providing state-of-the-art facilities for comprehensive patient care. We are equipped with a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG (Electroencephalography) monitoring of patients with epilepsy.
- Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG:
Leading the way in technological innovation, our center is the first in the continent to launch Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG procedures, ensuring enhanced precision and efficiency.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Pioneers in minimally invasive epilepsy surgery, particularly radiofrequency ablation, with the distinction of having performed the largest number of ablations in the country.
- Largest Number of Stereo EEG Evaluations:
Setting a benchmark, the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has conducted the largest number (more than 290 cases) of stereo EEG evaluations in the country.
- Stereo EEG Innovation:
Pioneering the development of a stereo EEG program, Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is the first in the country to implement this advanced diagnostic approach.
- Cutting-edge EEG Technology:
Equipped with a High-Density EEG (256 channel) system, ensuring precision and accuracy in monitoring and diagnosing epilepsy cases.
- Extensive Surgical Expertise:
Successfully completed over 1000 cases of epilepsy surgeries, showcasing a wealth of surgical experience and expertise.
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Cases:
Offering advanced treatment options, our center is at the forefront of addressing medically refractory epilepsy cases through deep brain stimulation.
Out patient Services
At the heart of our commitment to epilepsy care are our four full-time epileptologists. These seasoned neurologists, equipped with fellowship training and expertise in modern epilepsy management, are readily available for consultations, ensuring patients receive timely and specialized care.
First-Time Patient Focus:
Recognizing the significance of understanding each patient's history, we prioritize taking detailed histories and conducting clinical examination for patients visiting our center for the first time. This personalized approach allows us to tailor our care to the specific needs of each patient.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
Any Complex epilepsy case is discussed in a multidisciplinary team meeting. This team is comprised of epileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, neuroradiologists, nuclear medicine physicians, neuropsychologists, neuropsychiatrists, neuropathologists, geneticists, neuroscientists, neurotechnologists, epilepsy nurses, and nutrition experts. Our team engages in thorough discussions,ensuring a holistic understanding of the patient's condition. This collaborative approach allows for comprehensive care planning and execution.
Outpatient Excellence:
Our outpatient services extend beyond routine care. We provide special clarification for cases of suspected epilepsy, ensuring accurate diagnoses and personalized long-term care plans. Complex and difficult-to-treat cases find dedicated attention from our expert team meetings.
Why choose us?
At the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE), we stand out as a premier institution dedicated to transforming the lives of individuals affected by epilepsy.
Leading Expertise: Our centre boasts a team of renowned epileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, neuroradiologists, nuclear medicine physicians, neuropsychologists, neuropsychiatrists, neuropathologists, geneticists, and neuroscientists, each with specialized training and expertise in the modern management of epilepsy. With a focus on cutting-edge practices, we lead the way in providing advanced care.
State-of-the-Art Facilities: Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is equipped with the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in India, featuring a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG monitoring.
Innovative Treatments: From minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries to revolutionary therapies like Deep Brain Stimulation, we offer a spectrum of innovative treatments.
Comprehensive Patient Support: A team of four full-time epileptologists is always available for consultations, providing specialized care for patients with epilepsy. Our outpatient services focus on clarifying suspected epilepsy cases and offering long-term care, particularly for complex, difficult-to-treat cases.
What we offer
The Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi, is not just a medical facility; it's a beacon of hope and comprehensive care for individuals grappling with epilepsy.
Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit: Our 15-bedded unit is dedicated to long-term Video-EEG monitoring, providing a thorough understanding of epilepsy patterns for precise diagnosis and treatment.
Cutting-Edge Technology: With the country's largest epilepsy monitoring unit and the first Stereo EEG program, we embrace technology to enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. The use of Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG showcases our commitment to progressive methodologies.
Robotic Assisted Intracranial EEG (ICEEG) and Stereo-EEG:
Our approach initially involves using noninvasive methods to identify the seizure source in the brain, aiming to facilitate curative surgery. However, these noninvasive techniques often lack the precision needed for effective surgical intervention, a factor contributing to surgical failures worldwide. To overcome this, our center has been at the forefront of developing advanced intracranial EEG methods. These sophisticated techniques are designed to tackle the most complex cases, thereby boosting our success rates. Notably, this advanced method allows for the placement of electrodes inside the brain without necessitating the opening of the skull.
Multidisciplinary Approach: A team of experts collaborates to offer personalized care. From history-taking for first-time visitors to pre-surgical consultations, our multi-disciplinary team ensures a holistic approach to patient well-being.
Services Offered
Inpatient Services and Epilepsy Monitoring Unit (EMU)
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is equipped with a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG (Electroencephalography) monitoring of patients with epilepsy. The unit is staffed full-time with nurses trained in detection and management of seizures and neurotechnologists trained in advanced EEG techniques. Equipped with the latest advances in EEG recording, the EMU is the heart of the epilepsy centre and accurate diagnosis, and localization of seizures is key for leading to a successful cure.


256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI)
256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI) is a sophisticated technique that combines advanced signal processing and imaging methods to localize the brain circuits involved in the generation and propagation of seizures.
In this process, a 256-channel high-density EEG system, a EGI Magstim from the USA, is used to record the brain's electrical activity in patients with epilepsy. This recording, which typically lasts between 4 to 8 hours, captures a detailed and comprehensive map of brain activity.
During a thorough review of this EEG data, epileptic activities are identified. Following this, an electrical model of the patient's head is constructed using data from the patient’s volumetric MRI. The final step involves the application of detailed mathematical inverse solutions to localize the area of the brain responsible for generating epileptic activity. This advanced localization technique allows for a much more precise identification of the seizure focus than traditional methods.
By utilizing 256-channel high-density EEG and ESI, our centers can offer a more targeted and effective approach to diagnosing and treating epilepsy, potentially leading to better outcomes and more personalized care for patients.
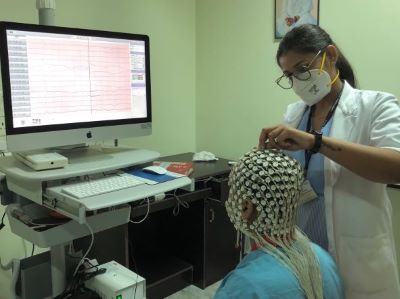
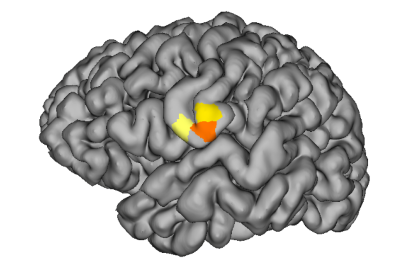
Neuroimaging Facilities
Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art neuroimaging technologies, including a 3 Tesla MRI, 3T MRI PET scanner, and Brain PET, offering advanced and detailed insights into epilepsy. These tools are essential for identifying the extent and characteristics of brain anomalies, thereby informing treatment strategies. Integral to our team are two dedicated full-time radiologists and a nuclear medicine expert, who contribute their skills and knowledge during bi-weekly pre-surgical epilepsy conferences at the AACE. Beyond PET scans, our nuclear medicine department collaborates with the EMU team, including epileptologists, nurses, and neurotechnologists, to conduct Ictal SPECT (Ictal Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). This intricate procedure, involving the injection of a radioactive tracer at the seizure's onset and subsequent brain blood flow imaging, is critical for pinpointing the seizure origin before surgical intervention.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a brain scanning method that shows which parts of the brain are active. When a brain area is more active, it uses more energy and oxygen. The fMRI measures changes in blood flow related to this activity. It uses the BOLD technique, which detects differences in magnetic signals from blood with and without oxygen. Areas with more oxygen-rich blood appear differently on the scan than those with less oxygen. This helps to see which parts of the brain are working during certain tasks. fMRI is especially useful for planning brain surgeries, as it can map important functions like language to avoid damaging them during surgery. It can also show how different brain areas are connected and work together, which is helpful in understanding conditions like epilepsy.
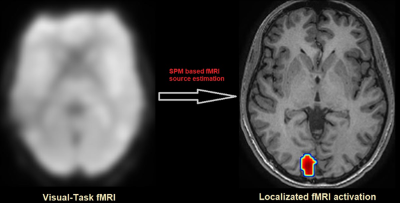
Wada Test
The Wada Test involves injecting a drug into the arteries of the brain to evaluate language and memory functions. This procedure helps determine which hemisphere of the brain is responsible for these specific cognitive functions, which is vital for planning surgical procedures and preserving crucial cognitive abilities during the treatment of epilepsy.
Extraoperative Intracranial EEG (ICEEG) Monitoring & Stereo-EEG
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring and Stereo-EEG represent advanced techniques in epilepsy treatment, particularly when noninvasive methods fail to provide precise information for curative surgery. These limitations in noninvasive approaches often contribute to surgical failures worldwide. Recognizing this, advanced intracranial EEG techniques have been developed and utilized to handle the most challenging cases, increasing success rates in epilepsy surgery.
At the Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE), over 300 ICEE surgeries have been performed using invasive monitoring, showcasing the center's commitment to addressing complex epilepsy cases. Notably, AACE is the first in India to develop and actively implement Stereo-EEG, a technique that involves the minimally invasive insertion of fine electrodes into the brain. This method enables safe targeting and monitoring of electrical activity throughout the brain, revealing the structures and networks responsible for seizures without the need for open skull surgery.
Today, this procedure is performed robotically at AACE, further enhancing its precision and safety. The use of Stereo-EEG, particularly in a robotic-assisted format, represents a significant advancement in epilepsy surgery, allowing for more accurate seizure focus detection and potentially improving patient outcomes in the most difficult cases.
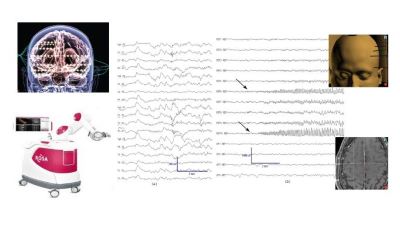
Functional Brain Mapping
Functional Brain Mapping is a sophisticated technique used in the treatment of epilepsy and other neurological conditions. In this process, electrodes are surgically implanted into the brain. These electrodes play a crucial role in accurately mapping various brain areas responsible for essential functions such as speech, movement, sensation, and vision.
The data gathered from this mapping is invaluable for surgical planning. It enables neurosurgeons to precisely identify and preserve areas of the brain that are critical for maintaining these vital functions. Simultaneously, it helps in accurately locating and removing the area of the brain that is responsible for seizures.
This technique is particularly important in epilepsy surgery, where the goal is to eliminate seizure activity without compromising the patient's quality of life. By identifying functional areas of the brain, surgeons can tailor their surgical approach to minimize the risk of impairing critical brain functions while effectively treating the epilepsy.
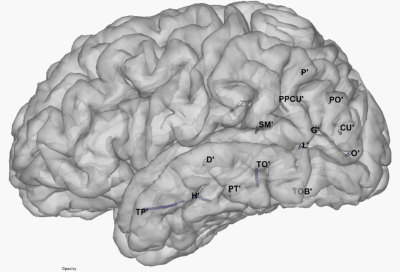
Our Philosophy
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is rooted in a patient-centric approach and a commitment to excellence in epilepsy care. Living with epilepsy can be challenging and we believe in standing by our patients, offering encouragement, and fostering a sense of community.
Individualized Care: Recognizing that epilepsy is a varied and complex condition, we prioritize individualized care plans. Our treatments are tailored to each patient's unique needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Holistic Wellness: Beyond medical interventions, we emphasize the overall well-being of our patients. Our approach considers not only the physical aspects of epilepsy but also the emotional and psychological dimensions, fostering a holistic healing environment.
Innovation and Research: Striving for continuous improvement, we actively engage in research and adopt innovative practices. This commitment positions us as leaders in the field, offering patients access to the latest advancements in epilepsy care.
Academy
- B.Sc. Neuroelectrophysiology
- M.Sc. Neuroelectrophysiology
- PhD program in epilepsy
Gallery


Facilities Available
Surgical program
The surgical program at the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has successfully completed over 1000 surgeries since its inception and has quickly emerged as one of the leading referral centres for epilepsy surgery. Most epilepsy surgeries are performed to remove the specific structures within the brain that give rise to the patient’s seizures. After a detailed pre-surgical evaluation through the EMU and imaging centres, the team meets twice weekly, dedicating time to evaluate and form a surgical plan for each individual patient.
The unique strengths of the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy surgical programme include
- First in India for Robotic insertion of Stereo EEG electrodes for mapping seizure focus and brain functions.
- Facilities and expertise in awake surgery to maximize the successful outcomes in brain surgeries (more than 100 awake surgeries successfully completed to date)
- Extraoperative brain mapping
- Image-guidance technology
- Advanced electrocorticography
- Two trained epilepsy surgeons experienced in all techniques of adult and pediatric epilepsy surgery.
As a result of the multi-modal, labor-intensive approach by a highly skilled team, the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has already demonstrated higher seizure-freedom rates (80-90 %), well above the reported norms.
Brain Mapping Laboratory
What sets this laboratory apart is the seamless collaboration between the clinical team and the engineers and scientists. This integrated approach significantly enhances our ability to conduct pre-surgical evaluations using cutting-edge techniques in signal and image processing, particularly for intricate epilepsy cases. The laboratory team includes Dr. Harilal Parasuram, a computational neurologist with a Ph.D. in Computational Neuroscience from Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, and Romero Arakulam, who holds a Master's degree in Biomedical Engineering from the University of Strathclyde in Glasgow, UK.
Advanced Signal analysis
Stereo-EEG analysis using Epileptogenicity Rank (ER)
In our lab, we use a special technique called Stereo-EEG analysis with Epileptogenicity Rank (ER) for epilepsy patients. ER is an improved way to measure how likely different parts of the brain are to cause seizures. It does this by looking at the strength and pattern of brain signals over time and space. Basically, ER adds a new layer to an existing method (EI) by considering not just when and how brain activity changes over time, but also where these changes happen in the brain. This helps us to tell apart the exact starting point of a seizure from where it spreads. We do this by noticing sudden changes in the frequency of brain waves over time and how far these changes are from the part of the brain where the seizure begins. This method is really helpful in understanding the epileptic network more effectively.
High frequency oscillation analysis
High-frequency oscillations (HFOs) are brainwave patterns that occur during complex activities like language processing, planning movements, and forming memories. Interestingly, parts of the brain involved in epilepsy, known as the epileptogenic network, tend to produce these HFOs at higher rates, but in a way that's not typical, known as 'pathological HFOs'. At our center, we focus on studying these HFOs, particularly in two specific ranges: Ripples (80-250Hz) and Fast Ripples (250-600 Hz). By analyzing these, we can determine how often HFOs occur in specific brain regions. This information is crucial because it helps us predict the area of the brain where epilepsy originates, known as the epileptogenic zone. This analysis is a key part of understanding and treating epilepsy more effectively.
Advanced Image Analysis:
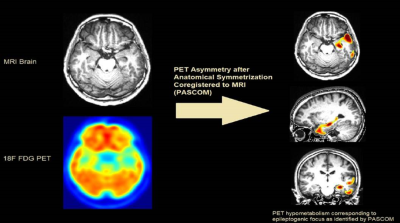
PASCOM - Advanced PET Analysis:
In our center, we use a specialized PET scan analysis called 18F FDG PET, which is crucial for examining patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). PET scans show brain metabolism by displaying varying intensities on the images. For patients with epilepsy, these scans often reveal areas of reduced metabolism, known as hypometabolism, which are key indicators of the epileptogenic zone (the area causing seizures).
Typically, PET scans are examined visually, comparing one side of the brain to the other to spot these areas of reduced metabolism. However, this process can be greatly improved with the help of computational tools. That's why we've developed a new technique called PASCOM (PET Asymmetry after Anatomical Symmetrization Coregistered on MRI). PASCOM automatically detects these regions of hypometabolism in PET scans without needing to compare them to control data, which is often required in other automated techniques. This independence makes PASCOM particularly effective for analyzing PET scans of both children and adults, enhancing our ability to locate the epileptogenic zone accurately and efficiently.
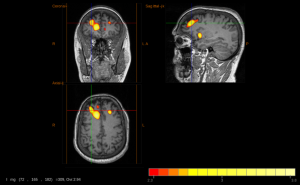
Subtraction Ictal SPECT CO-registered to MRI (SISCOM).
Subtraction Ictal SPECT Co-registered to MRI (SISCOM) is a method used to find the exact location of seizure activity in the brain for people with hard-to-treat epilepsy. It involves four main steps: aligning two SPECT scans for comparison, adjusting image clarity, highlighting differences between seizure and non-seizure images, and combining these images with MRI scans for a detailed view. This process is better than just looking at regular seizure-time SPECT scans because it gives a clearer picture of which brain areas are involved in the epilepsy, helping doctors plan treatment more effectively.
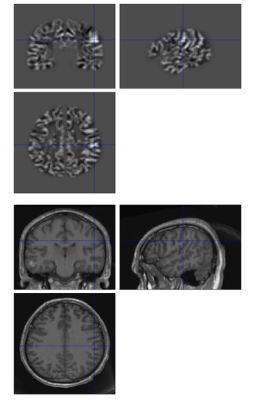
Voxel Based Morphometry Analysis for MRI lesion detection
This is a high-tech method for analyzing MRI images to spot brain lesions. It involves comparing the brain's grey and white matter with a big database of normal brain scans. This comparison creates a detailed 3D map that shows areas where the brain looks different from usual. It's a great way to find lesions that might not be easily seen in standard MRI reviews.
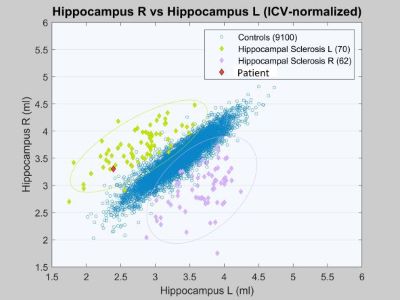
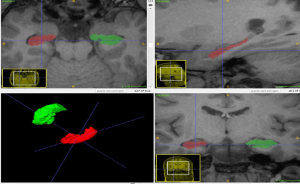
Hippocampal volumetry
Hippocampal Volumetry: This technique helps detect subtle forms of temporal lobe epilepsy. We carefully measure the size of the hippocampus (a brain area) on both sides using T1-weighted MRI images. This is done with the help of a detailed brain atlas. We then compare these measurements with the typical sizes expected for someone's age. This comparison can reveal any unusual changes in the hippocampus that might be linked to epilepsy.
Fellowship Programmes/Trainings
- Fellowships in Epileptology
Centre offers one-year postdoctoral clinical epilepsy fellowship programme: yearly intake of 2 candidates.
For details, contact Dr.Siby Gopinath
- Fellowships in Stereotactic/Functional Neurosurgery
Centre offers two-year postdoctoral epilepsy surgery fellowship programme: yearly intake of 1 candidate.
For details, contact Dr. Ashok Pillai
Courses
- Research Training Programs
The center provides an opportunity to participate in research and join the Ph.D. program in epilepsy. The center also provides internships for master’s/bachelor students from engineering /computer science / computational biology backgrounds.
For details, please contact Dr. Harilal Parasuram
FAQS
Epilepsy is a chronic medical condition marked by recurrent seizures, caused by abnormal electrical discharges in the brain.
Epilepsy is a condition prone to epileptic seizures or "fits." Anyone with two or more unprovoked seizures is considered to have epilepsy.
Neurologists, specializing in the brain and nervous system, and some become epileptologists, experts in epilepsy diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis is based on medical history, physical exams, and often requires an EEG. Brain imaging tests like MRI scans may also be necessary.
Women with epilepsy can have healthy children with proper prenatal care. Medication adjustments may be needed, and abrupt discontinuation can harm both the mother and baby.
Yes, fits in the first month of life are not uncommon. Causes are often metabolic abnormalities, and many infants don't develop epilepsy later.
Epilepsy is usually not caused by mental stress. However, stress can worsen seizures in those with epilepsy.
Yes, people with epilepsy can marry. However, it's essential to inform the prospective partner and make decisions based on seizure control.
Most mothers with epilepsy can safely breastfeed while taking their anti-epileptic drugs. Consultation with the treating doctor is advised in case of any issues.
For well-controlled epilepsy, a check-up once every 3-4 months is generally sufficient. Individuals with poorly controlled seizures or on multiple drugs may require more frequent visits. Special situations like epilepsy during pregnancy, in the elderly, or recurrent febrile convulsions may necessitate more frequent medical appointments.
Collaborations
International Collaborations
- Computational analysis for MRI lesion detection using Voxel-based Morphometry - Dr. Hans-Jürgen Huppertz Swiss Epilepsy Clinic, Switzerland.
- Multi-centric study on automated MRI lesion detection in epilepsy surgery patients. - Dr. Konrad Wagstyl and Team, Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging, University College London, UK.
National Collaboration - Intracranial-EEG monitoring, functional and behavioral mapping of cognition - Dr. SridharanDevarajan, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
Research Collaborations
- Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy practice in India: A tripartite survey
- Association of Child Neurology – Indian Epilepsy Society Expert Committee. Association of Child Neurology (AOCN) - Indian Epilepsy Society (IES) Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of West Syndrome.
- Swiss epilepsy center, Zurich, EU for developing research tools for MRI lesion detections.
- Multi-centric study on Human Intracerebral EEG Platform.
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, for magnetoencephalography (MEG) studies.
Achievements
- India's Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit:
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy holds the distinction of having the most extensive epilepsy monitoring unit in India. - Country's largest number of minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries.
- Successfully completed over 1000 surgeries, showcasing expertise in minimally invasive techniques
- The center is the first in the continent to start Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG.
- First in India to house a high-density EEG system within Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy
- Brain Mapping Laboratory: A first-of-its-kind laboratory in India, integrating the expertise of scientists and clinicians for a more comprehensive neurological understanding.
- First in the Country for Stereo EEG Program:
- Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is the first center in India to develop and actively utilize the groundbreaking technique of Stereo-EEG.
- National record for conducting the maximum number of intracranial EEG procedures using the special Stereo-EEG technique.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI)
ESI is an advanced signal and image-based technique used to localize the brain circuit involved in seizure generation and propagation. In this technique, a 256-channel HD EEG is recorded from the patient’s brain for about 4-8 hours. In a careful review the epileptic activity will be identified. Following this, an electrical model patient head model will be constructed from the patient’s volumetric MRI. Finally, the brain area which generates the epileptic activity is localized using detailed mathematical inverse solutions. In our center, we have 256-channel high density EEG (EGI Magstim, USA) to conduct ESI studies in our epilepsy patients.
Neuroimaging facilities
Advanced analysis of epilepsy requires precise imaging - high strength MRI (3 Tesla MRI), 3T MRI PET scanner and Brain PET (Positron Emission Tomography) form the cornerstone of epilepsy imaging. The centre is equipped with a GE Discovery 750 W Silent 3T MRI, Siemens 3T MRI PET scanner and GE Discovery PET 8 slice CT scanner. Two full-time radiologists and a full-time nuclear medicine specialist form part of the core-group in the AACE and provide their services and expertise in the twice weekly pre-surgical epilepsy conferences. In addition to PET imaging, the nuclear medicine department in conjunction with the EMU team of epileptologists, nurses and neurotechnologists are able to perform the difficult task of Ictal SPECT (Ictal Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). This study involves injection of a radioactive tracer at the onset of the patient’s seizures followed by imaging of the blood flow changes in the brain, helps to localize the focus responsible for seizures prior to surgical removal.
Functional MRI
Functional MRI, or fMRI, is a brain imaging technique that helps us understand brain activity by tracking changes in blood flow. When a part of the brain is more active, it uses more oxygen, and fMRI detects this change. The method relies on the difference in magnetic signals from oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood. This allows fMRI to show which areas of the brain are involved in specific activities/functions, like language. It's useful for planning surgeries to avoid damaging important brain areas. fMRI can also show how different brain regions connect and communicate in a resting state, which helps in understanding conditions like epilepsy.
Wada
Uses administration of a drug directly into the arteries of the brain to confirm the side of the brain involved in language and memory.
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring & Stereo-EEG
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring and Stereo-EEG represent cutting-edge techniques we utilize to pinpoint the origins of seizures within the brain. Initially, we attempt to identify the source of seizures through non-invasive methods, aiming to achieve successful surgical outcomes. However, these conventional methods sometimes fall short in providing adequate information for effective surgery, a limitation that contributes to surgical failures globally. To enhance our success rates, particularly in complex cases, our center has been at the forefront of employing intracranial EEG from the outset, with a special emphasis on Stereo-EEG. We have conducted over 290 surgeries utilizing these sophisticated methods, establishing ourselves as pioneers in Stereo-EEG in India and leading in the number of such procedures nationwide.
Stereo-EEG is a minimally invasive approach involving the precise placement of electrodes within the brain. These electrodes enable us to meticulously track and analyze the brain's electrical activity, accurately identifying the specific areas and networks responsible for seizures. This technique allows for the detection of the seizure source without the need for open skull surgery. Presently, this procedure is executed with robotic assistance at our center, enhancing its precision and safety.
Functional Brain Mapping
Electrodes implanted into the brain are used to precisely map the areas of the brain involved in different functions like speaking, moving, sensations, vision. This information is then used to safely preserve important brain functions while removing the area responsible for the seizures.
Outreach Program
- Peripheral clinics- Kanghangad, Kerala
- Tribal outreach clinic Wayanad, Kerala
- Charity channels- free epilepsy surgery included.
Treatments
Treatment plays a crucial role in helping individuals diagnosed with epilepsy manage and control seizures. The following approaches are employed for effective epilepsy management:
Medication
Most people with epilepsy can achieve seizure freedom by taking anti-seizure medicines.
Finding the right medicine and dosage may require a gradual adjustment, considering factors such as seizure type, frequency, age, and overall health.
It's essential to take medicines as prescribed by our epileptologists, consult your doctor before making changes, and never stop medication without professional advice.
Surgery
Epilepsy surgery becomes an option when medicines fail to provide sufficient seizure control.
Surgeons remove the specific brain area responsible for seizures, guided by tests ensuring minimal impact on vital functions.
Minimally invasive approaches, such as MRI-guided laser ablation, offer alternatives when traditional surgery poses risks.
Post-surgery, some individuals may need to continue medication, but with the potential for reduced doses.
Other Therapies
- Minimally invasive surgeries: We use techniques such as radiofrequency ablation to target and eliminate the source of epilepsy in the brain. This method is particularly effective for conditions like hypothalamic hamartoma and other types of epilepsy where preserving brain function is crucial. The procedure doesn't require opening the skull, making it less invasive. Patients typically can leave the hospital within 1-2 days after the procedure, highlighting its minimal recovery time.
- Deep Brain Stimulation: Electrodes implanted in the brain send electrical pulses to reduce seizures, often used when medication is ineffective.
- Ketogenic Diet : A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can reduce seizures when medications are ineffective. The body breaks down fats for energy, leading to chemical changes that may suppress seizures. Supervision by healthcare professionals is crucial to ensure proper nutrition and manage potential side effects. Our team ensures that the patient follows a proper diet and suggests customized diet plans for the patients.
Contact Us
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE),
Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences,
AIMS P. O, Kochi, Kerala 682041
Phone: 0484 – 2851310 / 9400998559
For epilepsy consultation appointments
Phone: 0484 6682100
For epilepsy surgery appointments
Ms. Nayana
Phone: 9400998546
Email: mswneurosurgery@aims.amrita.edu
Our Team
Romero Arakhalam
Research Scholar

Dr. Balveen Singh
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow
Dr. Nisha Nithyanand Shenoy
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Gopalakrishnan G.
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Dr. Nivedita
Ketogenic Diet Clinic

Ms. Sonu Ravindran
Neurotechnologists

Akshaya Raman
Neurotechnologists

Kavitha
Epilepsy Nurse-in-Charge

Nayana
Epilepsy Co-ordinator
Our Past Fellow

Dr. Abhishek Gohel
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Rutul Shah
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. SagariGullapalli
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Harish Jayakumar
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Amit Kumar Agarwal
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. S. Muthukani
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Prashant Makhija
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. PushkaranJayapaul
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Dr. Sumana B Pallegar
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Mr. Shameer Aslam
Past Research Faculty
Overview
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is a pioneering centre committed to the relentless pursuit of upgrading the treatment of epilepsy. Established in February 2010, our centre has become a beacon of hope for individuals affected by epilepsy all around the world.
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi has evolved into a hub that extends its healing touch to patients hailing from all corners of India, the Middle East, Africa, Asia Minor, and various Southeast Asian countries
Beyond serving as a premier treatment facility, Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has taken on the responsibility of knowledge dissemination and skill enhancement. The center has also emerged as an advanced epilepsy teaching centre for training neurologists, neurosurgeons, psychologists and technicians in the field - providing a strategy to help contain this globally devastating illness.
Our multidisciplinary team collaborates seamlessly to provide personalized and effective treatment. We recognize the profound impact that epilepsy can have on individuals and their families, and we are committed to offering not just medical treatment, but also support and educate our patients to empower and lead fulfilling lives.
Key Features:
- Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE) has the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in the country.
- AACE equipped with a high-density EEG system, a unique high-resolution scalp EEG
- India’s first in conducting the largest number of minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries
- Brain mapping research laboratory with scientists in collaboration with the clinicians
- Completed over 1000 epilepsy surgeries
- AACE is the first centre in India to develop and actively practice the technique of Stereo-EEG.
- Maximum number of intracranial EEG with this special technique of Stereo-EEG in this country
Disease Treated
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common disease that afflicts nearly 60 million people worldwide of which 6 million (10%) reside in India. Apart from being a physical disease, epilepsy has a strong mental and social implication. This disease adversely affects women with pregnancy and is an important contributor of learning disability in children. The incidence of divorce among epilepsy patients is on the rise. The unpredictability of epileptic attack leaves the patients helpless and most of the time at the mercy of others.
Drug-resistant epilepsy
Approximately one-third of patients whose seizures are not responsive to AEDs (drug-resistant epilepsies), can be cured of their seizures by surgical treatment (epilepsy surgery). Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE) provides comprehensive care to individuals who suffer from epilepsy. The Centre celebrated the successful completion of over 1000 epilepsy surgeries till date. Our team of experts include adult epileptologists, paediatricepileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, radiologists, nuclear medicine physician, neuroscientists, neuropathologist, neuropsychologist, medical social workers and dieticians.
Features
- Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit in the Country:
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi has the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in the country, providing state-of-the-art facilities for comprehensive patient care. We are equipped with a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG (Electroencephalography) monitoring of patients with epilepsy.
- Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG:
Leading the way in technological innovation, our center is the first in the continent to launch Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG procedures, ensuring enhanced precision and efficiency.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Pioneers in minimally invasive epilepsy surgery, particularly radiofrequency ablation, with the distinction of having performed the largest number of ablations in the country.
- Largest Number of Stereo EEG Evaluations:
Setting a benchmark, the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has conducted the largest number (more than 290 cases) of stereo EEG evaluations in the country.
- Stereo EEG Innovation:
Pioneering the development of a stereo EEG program, Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is the first in the country to implement this advanced diagnostic approach.
- Cutting-edge EEG Technology:
Equipped with a High-Density EEG (256 channel) system, ensuring precision and accuracy in monitoring and diagnosing epilepsy cases.
- Extensive Surgical Expertise:
Successfully completed over 1000 cases of epilepsy surgeries, showcasing a wealth of surgical experience and expertise.
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Cases:
Offering advanced treatment options, our center is at the forefront of addressing medically refractory epilepsy cases through deep brain stimulation.
Out patient Services
At the heart of our commitment to epilepsy care are our four full-time epileptologists. These seasoned neurologists, equipped with fellowship training and expertise in modern epilepsy management, are readily available for consultations, ensuring patients receive timely and specialized care.
First-Time Patient Focus:
Recognizing the significance of understanding each patient's history, we prioritize taking detailed histories and conducting clinical examination for patients visiting our center for the first time. This personalized approach allows us to tailor our care to the specific needs of each patient.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration:
Any Complex epilepsy case is discussed in a multidisciplinary team meeting. This team is comprised of epileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, neuroradiologists, nuclear medicine physicians, neuropsychologists, neuropsychiatrists, neuropathologists, geneticists, neuroscientists, neurotechnologists, epilepsy nurses, and nutrition experts. Our team engages in thorough discussions,ensuring a holistic understanding of the patient's condition. This collaborative approach allows for comprehensive care planning and execution.
Outpatient Excellence:
Our outpatient services extend beyond routine care. We provide special clarification for cases of suspected epilepsy, ensuring accurate diagnoses and personalized long-term care plans. Complex and difficult-to-treat cases find dedicated attention from our expert team meetings.
Why choose us?
At the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE), we stand out as a premier institution dedicated to transforming the lives of individuals affected by epilepsy.
Leading Expertise: Our centre boasts a team of renowned epileptologists, epilepsy surgeons, neuroradiologists, nuclear medicine physicians, neuropsychologists, neuropsychiatrists, neuropathologists, geneticists, and neuroscientists, each with specialized training and expertise in the modern management of epilepsy. With a focus on cutting-edge practices, we lead the way in providing advanced care.
State-of-the-Art Facilities: Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is equipped with the largest epilepsy monitoring unit in India, featuring a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG monitoring.
Innovative Treatments: From minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries to revolutionary therapies like Deep Brain Stimulation, we offer a spectrum of innovative treatments.
Comprehensive Patient Support: A team of four full-time epileptologists is always available for consultations, providing specialized care for patients with epilepsy. Our outpatient services focus on clarifying suspected epilepsy cases and offering long-term care, particularly for complex, difficult-to-treat cases.
What we offer
The Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy at Amrita Hospital, Kochi, is not just a medical facility; it's a beacon of hope and comprehensive care for individuals grappling with epilepsy.
Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit: Our 15-bedded unit is dedicated to long-term Video-EEG monitoring, providing a thorough understanding of epilepsy patterns for precise diagnosis and treatment.
Cutting-Edge Technology: With the country's largest epilepsy monitoring unit and the first Stereo EEG program, we embrace technology to enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness. The use of Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG showcases our commitment to progressive methodologies.
Robotic Assisted Intracranial EEG (ICEEG) and Stereo-EEG:
Our approach initially involves using noninvasive methods to identify the seizure source in the brain, aiming to facilitate curative surgery. However, these noninvasive techniques often lack the precision needed for effective surgical intervention, a factor contributing to surgical failures worldwide. To overcome this, our center has been at the forefront of developing advanced intracranial EEG methods. These sophisticated techniques are designed to tackle the most complex cases, thereby boosting our success rates. Notably, this advanced method allows for the placement of electrodes inside the brain without necessitating the opening of the skull.
Multidisciplinary Approach: A team of experts collaborates to offer personalized care. From history-taking for first-time visitors to pre-surgical consultations, our multi-disciplinary team ensures a holistic approach to patient well-being.
Services Offered
Inpatient Services and Epilepsy Monitoring Unit (EMU)
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is equipped with a 15-bedded state-of-the-art unit dedicated to long-term Video-EEG (Electroencephalography) monitoring of patients with epilepsy. The unit is staffed full-time with nurses trained in detection and management of seizures and neurotechnologists trained in advanced EEG techniques. Equipped with the latest advances in EEG recording, the EMU is the heart of the epilepsy centre and accurate diagnosis, and localization of seizures is key for leading to a successful cure.


256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI)
256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI) is a sophisticated technique that combines advanced signal processing and imaging methods to localize the brain circuits involved in the generation and propagation of seizures.
In this process, a 256-channel high-density EEG system, a EGI Magstim from the USA, is used to record the brain's electrical activity in patients with epilepsy. This recording, which typically lasts between 4 to 8 hours, captures a detailed and comprehensive map of brain activity.
During a thorough review of this EEG data, epileptic activities are identified. Following this, an electrical model of the patient's head is constructed using data from the patient’s volumetric MRI. The final step involves the application of detailed mathematical inverse solutions to localize the area of the brain responsible for generating epileptic activity. This advanced localization technique allows for a much more precise identification of the seizure focus than traditional methods.
By utilizing 256-channel high-density EEG and ESI, our centers can offer a more targeted and effective approach to diagnosing and treating epilepsy, potentially leading to better outcomes and more personalized care for patients.


Neuroimaging Facilities
Our facility is equipped with state-of-the-art neuroimaging technologies, including a 3 Tesla MRI, 3T MRI PET scanner, and Brain PET, offering advanced and detailed insights into epilepsy. These tools are essential for identifying the extent and characteristics of brain anomalies, thereby informing treatment strategies. Integral to our team are two dedicated full-time radiologists and a nuclear medicine expert, who contribute their skills and knowledge during bi-weekly pre-surgical epilepsy conferences at the AACE. Beyond PET scans, our nuclear medicine department collaborates with the EMU team, including epileptologists, nurses, and neurotechnologists, to conduct Ictal SPECT (Ictal Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). This intricate procedure, involving the injection of a radioactive tracer at the seizure's onset and subsequent brain blood flow imaging, is critical for pinpointing the seizure origin before surgical intervention.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Functional MRI (fMRI) is a brain scanning method that shows which parts of the brain are active. When a brain area is more active, it uses more energy and oxygen. The fMRI measures changes in blood flow related to this activity. It uses the BOLD technique, which detects differences in magnetic signals from blood with and without oxygen. Areas with more oxygen-rich blood appear differently on the scan than those with less oxygen. This helps to see which parts of the brain are working during certain tasks. fMRI is especially useful for planning brain surgeries, as it can map important functions like language to avoid damaging them during surgery. It can also show how different brain areas are connected and work together, which is helpful in understanding conditions like epilepsy.

Wada Test
The Wada Test involves injecting a drug into the arteries of the brain to evaluate language and memory functions. This procedure helps determine which hemisphere of the brain is responsible for these specific cognitive functions, which is vital for planning surgical procedures and preserving crucial cognitive abilities during the treatment of epilepsy.
Extraoperative Intracranial EEG (ICEEG) Monitoring & Stereo-EEG
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring and Stereo-EEG represent advanced techniques in epilepsy treatment, particularly when noninvasive methods fail to provide precise information for curative surgery. These limitations in noninvasive approaches often contribute to surgical failures worldwide. Recognizing this, advanced intracranial EEG techniques have been developed and utilized to handle the most challenging cases, increasing success rates in epilepsy surgery.
At the Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE), over 300 ICEE surgeries have been performed using invasive monitoring, showcasing the center's commitment to addressing complex epilepsy cases. Notably, AACE is the first in India to develop and actively implement Stereo-EEG, a technique that involves the minimally invasive insertion of fine electrodes into the brain. This method enables safe targeting and monitoring of electrical activity throughout the brain, revealing the structures and networks responsible for seizures without the need for open skull surgery.
Today, this procedure is performed robotically at AACE, further enhancing its precision and safety. The use of Stereo-EEG, particularly in a robotic-assisted format, represents a significant advancement in epilepsy surgery, allowing for more accurate seizure focus detection and potentially improving patient outcomes in the most difficult cases.

Functional Brain Mapping
Functional Brain Mapping is a sophisticated technique used in the treatment of epilepsy and other neurological conditions. In this process, electrodes are surgically implanted into the brain. These electrodes play a crucial role in accurately mapping various brain areas responsible for essential functions such as speech, movement, sensation, and vision.
The data gathered from this mapping is invaluable for surgical planning. It enables neurosurgeons to precisely identify and preserve areas of the brain that are critical for maintaining these vital functions. Simultaneously, it helps in accurately locating and removing the area of the brain that is responsible for seizures.
This technique is particularly important in epilepsy surgery, where the goal is to eliminate seizure activity without compromising the patient's quality of life. By identifying functional areas of the brain, surgeons can tailor their surgical approach to minimize the risk of impairing critical brain functions while effectively treating the epilepsy.

Our Philosophy
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is rooted in a patient-centric approach and a commitment to excellence in epilepsy care. Living with epilepsy can be challenging and we believe in standing by our patients, offering encouragement, and fostering a sense of community.
Individualized Care: Recognizing that epilepsy is a varied and complex condition, we prioritize individualized care plans. Our treatments are tailored to each patient's unique needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Holistic Wellness: Beyond medical interventions, we emphasize the overall well-being of our patients. Our approach considers not only the physical aspects of epilepsy but also the emotional and psychological dimensions, fostering a holistic healing environment.
Innovation and Research: Striving for continuous improvement, we actively engage in research and adopt innovative practices. This commitment positions us as leaders in the field, offering patients access to the latest advancements in epilepsy care.
Academy
- B.Sc. Neuroelectrophysiology
- M.Sc. Neuroelectrophysiology
- PhD program in epilepsy
Gallery


Facilities Available
Surgical program
The surgical program at the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has successfully completed over 1000 surgeries since its inception and has quickly emerged as one of the leading referral centres for epilepsy surgery. Most epilepsy surgeries are performed to remove the specific structures within the brain that give rise to the patient’s seizures. After a detailed pre-surgical evaluation through the EMU and imaging centres, the team meets twice weekly, dedicating time to evaluate and form a surgical plan for each individual patient.
The unique strengths of the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy surgical programme include
- First in India for Robotic insertion of Stereo EEG electrodes for mapping seizure focus and brain functions.
- Facilities and expertise in awake surgery to maximize the successful outcomes in brain surgeries (more than 100 awake surgeries successfully completed to date)
- Extraoperative brain mapping
- Image-guidance technology
- Advanced electrocorticography
- Two trained epilepsy surgeons experienced in all techniques of adult and pediatric epilepsy surgery.
As a result of the multi-modal, labor-intensive approach by a highly skilled team, the Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy has already demonstrated higher seizure-freedom rates (80-90 %), well above the reported norms.
Brain Mapping Laboratory
What sets this laboratory apart is the seamless collaboration between the clinical team and the engineers and scientists. This integrated approach significantly enhances our ability to conduct pre-surgical evaluations using cutting-edge techniques in signal and image processing, particularly for intricate epilepsy cases. The laboratory team includes Dr. Harilal Parasuram, a computational neurologist with a Ph.D. in Computational Neuroscience from Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, and Romero Arakulam, who holds a Master's degree in Biomedical Engineering from the University of Strathclyde in Glasgow, UK.
Advanced Signal analysis
Stereo-EEG analysis using Epileptogenicity Rank (ER)
In our lab, we use a special technique called Stereo-EEG analysis with Epileptogenicity Rank (ER) for epilepsy patients. ER is an improved way to measure how likely different parts of the brain are to cause seizures. It does this by looking at the strength and pattern of brain signals over time and space. Basically, ER adds a new layer to an existing method (EI) by considering not just when and how brain activity changes over time, but also where these changes happen in the brain. This helps us to tell apart the exact starting point of a seizure from where it spreads. We do this by noticing sudden changes in the frequency of brain waves over time and how far these changes are from the part of the brain where the seizure begins. This method is really helpful in understanding the epileptic network more effectively.
High frequency oscillation analysis
High-frequency oscillations (HFOs) are brainwave patterns that occur during complex activities like language processing, planning movements, and forming memories. Interestingly, parts of the brain involved in epilepsy, known as the epileptogenic network, tend to produce these HFOs at higher rates, but in a way that's not typical, known as 'pathological HFOs'. At our center, we focus on studying these HFOs, particularly in two specific ranges: Ripples (80-250Hz) and Fast Ripples (250-600 Hz). By analyzing these, we can determine how often HFOs occur in specific brain regions. This information is crucial because it helps us predict the area of the brain where epilepsy originates, known as the epileptogenic zone. This analysis is a key part of understanding and treating epilepsy more effectively.
Advanced Image Analysis:
PASCOM - Advanced PET Analysis:
In our center, we use a specialized PET scan analysis called 18F FDG PET, which is crucial for examining patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). PET scans show brain metabolism by displaying varying intensities on the images. For patients with epilepsy, these scans often reveal areas of reduced metabolism, known as hypometabolism, which are key indicators of the epileptogenic zone (the area causing seizures).
Typically, PET scans are examined visually, comparing one side of the brain to the other to spot these areas of reduced metabolism. However, this process can be greatly improved with the help of computational tools. That's why we've developed a new technique called PASCOM (PET Asymmetry after Anatomical Symmetrization Coregistered on MRI). PASCOM automatically detects these regions of hypometabolism in PET scans without needing to compare them to control data, which is often required in other automated techniques. This independence makes PASCOM particularly effective for analyzing PET scans of both children and adults, enhancing our ability to locate the epileptogenic zone accurately and efficiently.

Subtraction Ictal SPECT CO-registered to MRI (SISCOM).
Subtraction Ictal SPECT Co-registered to MRI (SISCOM) is a method used to find the exact location of seizure activity in the brain for people with hard-to-treat epilepsy. It involves four main steps: aligning two SPECT scans for comparison, adjusting image clarity, highlighting differences between seizure and non-seizure images, and combining these images with MRI scans for a detailed view. This process is better than just looking at regular seizure-time SPECT scans because it gives a clearer picture of which brain areas are involved in the epilepsy, helping doctors plan treatment more effectively.

Voxel Based Morphometry Analysis for MRI lesion detection
This is a high-tech method for analyzing MRI images to spot brain lesions. It involves comparing the brain's grey and white matter with a big database of normal brain scans. This comparison creates a detailed 3D map that shows areas where the brain looks different from usual. It's a great way to find lesions that might not be easily seen in standard MRI reviews.

Hippocampal volumetry
Hippocampal Volumetry: This technique helps detect subtle forms of temporal lobe epilepsy. We carefully measure the size of the hippocampus (a brain area) on both sides using T1-weighted MRI images. This is done with the help of a detailed brain atlas. We then compare these measurements with the typical sizes expected for someone's age. This comparison can reveal any unusual changes in the hippocampus that might be linked to epilepsy.


Fellowship Programmes/Trainings
- Fellowships in Epileptology
Centre offers one-year postdoctoral clinical epilepsy fellowship programme: yearly intake of 2 candidates.
For details, contact Dr.Siby Gopinath
- Fellowships in Stereotactic/Functional Neurosurgery
Centre offers two-year postdoctoral epilepsy surgery fellowship programme: yearly intake of 1 candidate.
For details, contact Dr. Ashok Pillai
Courses
- Research Training Programs
The center provides an opportunity to participate in research and join the Ph.D. program in epilepsy. The center also provides internships for master’s/bachelor students from engineering /computer science / computational biology backgrounds.
For details, please contact Dr. Harilal Parasuram
FAQS
Epilepsy is a chronic medical condition marked by recurrent seizures, caused by abnormal electrical discharges in the brain.
Epilepsy is a condition prone to epileptic seizures or "fits." Anyone with two or more unprovoked seizures is considered to have epilepsy.
Neurologists, specializing in the brain and nervous system, and some become epileptologists, experts in epilepsy diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis is based on medical history, physical exams, and often requires an EEG. Brain imaging tests like MRI scans may also be necessary.
Women with epilepsy can have healthy children with proper prenatal care. Medication adjustments may be needed, and abrupt discontinuation can harm both the mother and baby.
Yes, fits in the first month of life are not uncommon. Causes are often metabolic abnormalities, and many infants don't develop epilepsy later.
Epilepsy is usually not caused by mental stress. However, stress can worsen seizures in those with epilepsy.
Yes, people with epilepsy can marry. However, it's essential to inform the prospective partner and make decisions based on seizure control.
Most mothers with epilepsy can safely breastfeed while taking their anti-epileptic drugs. Consultation with the treating doctor is advised in case of any issues.
For well-controlled epilepsy, a check-up once every 3-4 months is generally sufficient. Individuals with poorly controlled seizures or on multiple drugs may require more frequent visits. Special situations like epilepsy during pregnancy, in the elderly, or recurrent febrile convulsions may necessitate more frequent medical appointments.
Collaborations
International Collaborations
- Computational analysis for MRI lesion detection using Voxel-based Morphometry - Dr. Hans-Jürgen Huppertz Swiss Epilepsy Clinic, Switzerland.
- Multi-centric study on automated MRI lesion detection in epilepsy surgery patients. - Dr. Konrad Wagstyl and Team, Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging, University College London, UK.
National Collaboration - Intracranial-EEG monitoring, functional and behavioral mapping of cognition - Dr. SridharanDevarajan, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
Research Collaborations
- Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy practice in India: A tripartite survey
- Association of Child Neurology – Indian Epilepsy Society Expert Committee. Association of Child Neurology (AOCN) - Indian Epilepsy Society (IES) Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of West Syndrome.
- Swiss epilepsy center, Zurich, EU for developing research tools for MRI lesion detections.
- Multi-centric study on Human Intracerebral EEG Platform.
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, for magnetoencephalography (MEG) studies.
Achievements
- India's Largest Epilepsy Monitoring Unit:
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy holds the distinction of having the most extensive epilepsy monitoring unit in India. - Country's largest number of minimally invasive epilepsy surgeries.
- Successfully completed over 1000 surgeries, showcasing expertise in minimally invasive techniques
- The center is the first in the continent to start Robotic Assisted Stereo EEG.
- First in India to house a high-density EEG system within Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy
- Brain Mapping Laboratory: A first-of-its-kind laboratory in India, integrating the expertise of scientists and clinicians for a more comprehensive neurological understanding.
- First in the Country for Stereo EEG Program:
- Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy is the first center in India to develop and actively utilize the groundbreaking technique of Stereo-EEG.
- National record for conducting the maximum number of intracranial EEG procedures using the special Stereo-EEG technique.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
256-channel High Density EEG and Electrical Source Localization (ESI)
ESI is an advanced signal and image-based technique used to localize the brain circuit involved in seizure generation and propagation. In this technique, a 256-channel HD EEG is recorded from the patient’s brain for about 4-8 hours. In a careful review the epileptic activity will be identified. Following this, an electrical model patient head model will be constructed from the patient’s volumetric MRI. Finally, the brain area which generates the epileptic activity is localized using detailed mathematical inverse solutions. In our center, we have 256-channel high density EEG (EGI Magstim, USA) to conduct ESI studies in our epilepsy patients.
Neuroimaging facilities
Advanced analysis of epilepsy requires precise imaging - high strength MRI (3 Tesla MRI), 3T MRI PET scanner and Brain PET (Positron Emission Tomography) form the cornerstone of epilepsy imaging. The centre is equipped with a GE Discovery 750 W Silent 3T MRI, Siemens 3T MRI PET scanner and GE Discovery PET 8 slice CT scanner. Two full-time radiologists and a full-time nuclear medicine specialist form part of the core-group in the AACE and provide their services and expertise in the twice weekly pre-surgical epilepsy conferences. In addition to PET imaging, the nuclear medicine department in conjunction with the EMU team of epileptologists, nurses and neurotechnologists are able to perform the difficult task of Ictal SPECT (Ictal Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography). This study involves injection of a radioactive tracer at the onset of the patient’s seizures followed by imaging of the blood flow changes in the brain, helps to localize the focus responsible for seizures prior to surgical removal.
Functional MRI
Functional MRI, or fMRI, is a brain imaging technique that helps us understand brain activity by tracking changes in blood flow. When a part of the brain is more active, it uses more oxygen, and fMRI detects this change. The method relies on the difference in magnetic signals from oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood. This allows fMRI to show which areas of the brain are involved in specific activities/functions, like language. It's useful for planning surgeries to avoid damaging important brain areas. fMRI can also show how different brain regions connect and communicate in a resting state, which helps in understanding conditions like epilepsy.
Wada
Uses administration of a drug directly into the arteries of the brain to confirm the side of the brain involved in language and memory.
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring & Stereo-EEG
Extraoperative intracranial EEG (ICEEG) monitoring and Stereo-EEG represent cutting-edge techniques we utilize to pinpoint the origins of seizures within the brain. Initially, we attempt to identify the source of seizures through non-invasive methods, aiming to achieve successful surgical outcomes. However, these conventional methods sometimes fall short in providing adequate information for effective surgery, a limitation that contributes to surgical failures globally. To enhance our success rates, particularly in complex cases, our center has been at the forefront of employing intracranial EEG from the outset, with a special emphasis on Stereo-EEG. We have conducted over 290 surgeries utilizing these sophisticated methods, establishing ourselves as pioneers in Stereo-EEG in India and leading in the number of such procedures nationwide.
Stereo-EEG is a minimally invasive approach involving the precise placement of electrodes within the brain. These electrodes enable us to meticulously track and analyze the brain's electrical activity, accurately identifying the specific areas and networks responsible for seizures. This technique allows for the detection of the seizure source without the need for open skull surgery. Presently, this procedure is executed with robotic assistance at our center, enhancing its precision and safety.
Functional Brain Mapping
Electrodes implanted into the brain are used to precisely map the areas of the brain involved in different functions like speaking, moving, sensations, vision. This information is then used to safely preserve important brain functions while removing the area responsible for the seizures.
Outreach Program
- Peripheral clinics- Kanghangad, Kerala
- Tribal outreach clinic Wayanad, Kerala
- Charity channels- free epilepsy surgery included.
Treatments
Treatment plays a crucial role in helping individuals diagnosed with epilepsy manage and control seizures. The following approaches are employed for effective epilepsy management:
Medication
Most people with epilepsy can achieve seizure freedom by taking anti-seizure medicines.
Finding the right medicine and dosage may require a gradual adjustment, considering factors such as seizure type, frequency, age, and overall health.
It's essential to take medicines as prescribed by our epileptologists, consult your doctor before making changes, and never stop medication without professional advice.
Surgery
Epilepsy surgery becomes an option when medicines fail to provide sufficient seizure control.
Surgeons remove the specific brain area responsible for seizures, guided by tests ensuring minimal impact on vital functions.
Minimally invasive approaches, such as MRI-guided laser ablation, offer alternatives when traditional surgery poses risks.
Post-surgery, some individuals may need to continue medication, but with the potential for reduced doses.
Other Therapies
- Minimally invasive surgeries: We use techniques such as radiofrequency ablation to target and eliminate the source of epilepsy in the brain. This method is particularly effective for conditions like hypothalamic hamartoma and other types of epilepsy where preserving brain function is crucial. The procedure doesn't require opening the skull, making it less invasive. Patients typically can leave the hospital within 1-2 days after the procedure, highlighting its minimal recovery time.
- Deep Brain Stimulation: Electrodes implanted in the brain send electrical pulses to reduce seizures, often used when medication is ineffective.
- Ketogenic Diet : A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can reduce seizures when medications are ineffective. The body breaks down fats for energy, leading to chemical changes that may suppress seizures. Supervision by healthcare professionals is crucial to ensure proper nutrition and manage potential side effects. Our team ensures that the patient follows a proper diet and suggests customized diet plans for the patients.
Contact Us
Amrita Advanced Centre for Epilepsy (AACE),
Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences,
AIMS P. O, Kochi, Kerala 682041
Phone: 0484 – 2851310 / 9400998559
For epilepsy consultation appointments
Phone: 0484 6682100
For epilepsy surgery appointments
Ms. Nayana
Phone: 9400998546
Email: mswneurosurgery@aims.amrita.edu
Our Team
Romero Arakhalam
Research Scholar

Dr. Balveen Singh
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow
Dr. Nisha Nithyanand Shenoy
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Gopalakrishnan G.
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Dr. Nivedita
Ketogenic Diet Clinic

Ms. Sonu Ravindran
Neurotechnologists

Akshaya Raman
Neurotechnologists

Kavitha
Epilepsy Nurse-in-Charge

Nayana
Epilepsy Co-ordinator
Our Past Fellow

Dr. Abhishek Gohel
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Rutul Shah
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. SagariGullapalli
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Harish Jayakumar
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Amit Kumar Agarwal
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. S. Muthukani
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. Prashant Makhija
Post-doctoral Epilepsy Fellow

Dr. PushkaranJayapaul
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Dr. Sumana B Pallegar
Past Post-doctoral Epilepsy Surgery Fellow

Mr. Shameer Aslam
Past Research Faculty


















